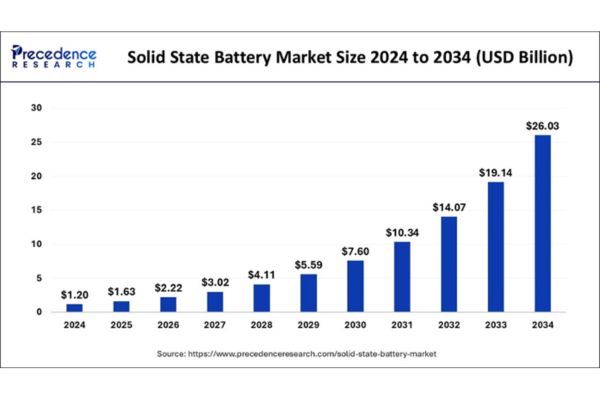
The global solid state battery market size is evaluated at USD 1.63 billion in 2025 and is predicted to be worth around USD 26.03 billion by 2034, growing at a remarkable CAGR of 36.03% from 2025 to 2034.
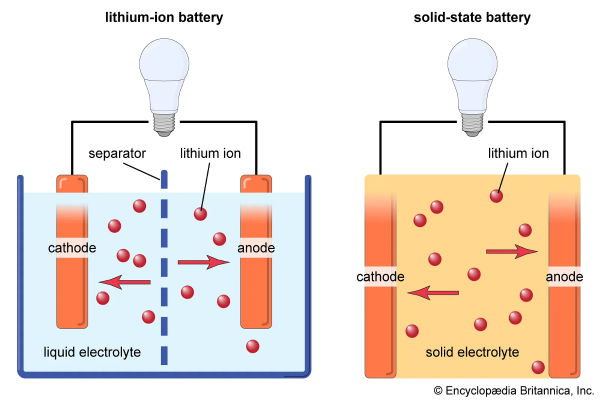
A solid-state battery (SSB) is a type of rechargeable battery that uses a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid or gel electrolytes found in conventional lithium-ion batteries. The solid electrolyte can be made from ceramics, sulfides, oxides, phosphates, or solid polymers, and it conducts ions between the battery’s electrodes. This design allows for the use of high-capacity materials like metallic lithium for the anode, resulting in potentially higher energy densities compared to traditional batteries.
Why is Asia Pacific leading the growth of the solid state battery market
Strong Demand from Key Industries: The region’s booming consumer electronics and electric vehicle (EV) sectors are major drivers. Asia Pacific, especially China, Japan, and South Korea, has a high concentration of electronics manufacturing and is the largest global market for EVs, which increasingly require advanced battery technologies like solid-state batteries for higher energy density, safety, and performance.
Robust R&D and Patent Leadership: Japan and South Korea are global leaders in solid-state battery research and development, with Japanese companies holding the majority of global patents in this field. Major corporations such as Toyota, Panasonic, and Samsung are investing heavily in innovation, with Japan alone accounting for around 68% of global solid-state battery patents.
Government Support and Incentives: Governments across Asia Pacific, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, are providing substantial support through investments, incentives, and regulatory frameworks aimed at promoting EV adoption, reducing carbon emissions, and advancing battery technology. These initiatives create a favorable environment for both research and commercialization.
Manufacturing Ecosystem and Skilled Workforce: The shift of production industries to emerging economies like China and India, combined with a large, skilled, and cost-effective workforce, strengthens the region’s manufacturing base. This supports rapid scaling and cost reduction in solid-state battery production.
Aggressive EV and Renewable Energy Policies: The region’s governments are setting ambitious targets for EV adoption and renewable energy integration, which directly increases demand for advanced energy storage solutions such as solid-state batteries.
International Investment and Collaborations: Asia Pacific is attracting significant domestic and international investment in battery manufacturing and technology development, further accelerating market growth.
Solid-State vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
| Feature | Solid-State Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
| Electrolyte Type | Solid (ceramic/polymer) | Liquid or gel |
| Energy Density | >350 Wh/kg | <300 Wh/kg |
| Safety | High (nonflammable) | Moderate (flammable risk) |
| Lifespan | Longer | Shorter |
| Charging Speed | Faster potential | Slower |
| Temperature Range | Wider | Limited |
| Commercial Availability | Limited, in development | Widely available |
Solid-state batteries differ from traditional lithium-ion batteries primarily in their significantly higher energy density. This advantage stems from the use of solid electrolytes, which allow for the incorporation of lithium metal anodes instead of the graphite anodes found in conventional lithium-ion cells. Lithium metal anodes have a much higher charge capacity, enabling solid-state batteries to store more energy in the same volume or weight compared to their lithium-ion counterparts.
Typical energy density values for solid-state batteries range from 250 to 800 Wh/kg, whereas lithium-ion batteries generally offer 160 to 250 Wh/kg. This means solid-state batteries can be up to 2–2.5 times more energy-dense than current lithium-ion designs, resulting in smaller, lighter batteries for a given capacity. The solid electrolyte also supports higher-voltage cathodes and enables more compact cell designs, further boosting energy density.
What materials are most promising for improving solid electrolyte stability
Garnet-Type Electrolytes
Garnet-type solid inorganic electrolytes, such as Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO), are increasingly recognized for their high stability, particularly in all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. These materials are valued for their broad electrochemical stability window and compatibility with lithium metal anodes.
Pyrochlore-Type Oxyfluorides
Recent discoveries include pyrochlore-type oxyfluoride materials, such as Li1.25La0.58Nb2O6F. These exhibit high ionic conductivity, low activation energy, and remarkable stability in air. Unlike many sulfide-based electrolytes, they are safe, non-toxic, and stable across a wide temperature range, making them strong candidates for next-generation batteries.
Lithium-Boron-Sulfur Electrolytes
Lithium-boron-sulfur compounds have demonstrated about twice the stability of leading solid electrolytes, offering both improved safety and performance. Their enhanced stability makes them promising for future battery designs.
Zeolite-Based Electrolytes
Zeolites are emerging as a promising option due to their excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and electrochemical stability. They also offer enhanced wettability and ionic conductivity, which are key for robust solid-state battery operation.
Ceramic-Type Lithium Tantalum Phosphate (LTPO)
LTPO electrolytes, synthesized via cold sintering, have shown excellent ionic conduction and stability, making them attractive for solid-state battery applications.
Polymer Electrolytes (e.g., Polyethylene Oxide, PEO)
Polyethylene oxide is the most widely used solid polymer electrolyte, known for its good chain flexibility and strong electrochemical stability with lithium metal.
Barrier/Interface Materials
Materials such as LiAlO2, LiTaO3, and LiNbO3 are often used as barrier layers at the electrode-electrolyte interface to improve stability, especially with high-voltage cathodes. These oxides possess wider stability windows and help prevent detrimental interfacial reactions.
Solid State Battery Market Top Companies
- BrightVolt Inc.
- Cymbet Corporation
- Solid Power Inc.
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Excellatron Solid State LLC
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Altair Nanotechnologies
- Quantumscape Corporation
- Apple Inc.
- Dyson Ltd.
Industry Leaders’ Announcements
- In April 2024, William Li, the CEO of Nio announced plans for developing 150kWh batteries for EVs from June/July of 2024. These EV batteries are expected to provide a driving range of 1000 kms on a single charge.
Recent Developments
- In December 2024, Factorial launched a 40Ah all-solid-state battery. These batteries are developed using dry coating process and finds application in automotive sector.
- In November 2024, Honda Motor Co., Ltd launched a new solid-state battery. These batteries are designed for future EVs.
- In August 2024, Samsung launched a new range of solid-state batteries. These batteries are designed for electric vehicles of Asia Pacific.