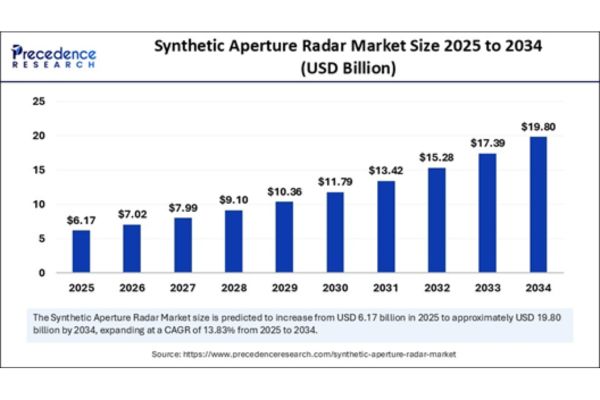
The synthetic aperture radar (SAR) market is experiencing unprecedented momentum, driven by its unmatched ability to deliver precise imaging regardless of lighting or weather conditions. Estimated at USD 5.42 billion in 2024, the market is expected to climb to USD 6.17 billion in 2025 and surge to USD 19.80 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 13.83%. This sharp growth curve is fueled by rising geopolitical tensions, an expanding defense budget globally, growing climate-related disaster response needs, and widespread adoption in commercial sectors like agriculture and infrastructure monitoring.
Why is Synthetic Aperture Radar Technology a Game-Changer for Global Observation?
At its core, SAR technology uses microwave pulses and leverages sensor motion to simulate a large antenna aperture, achieving ultra-high spatial resolution. Unlike traditional optical systems, SAR can image Earth’s surface through clouds, smoke, and darkness, making it an ideal choice for time-critical missions. Whether from satellites, aircraft, or UAVs, SAR ensures uninterrupted surveillance, making it a preferred tool in situations where consistent, weather-independent data is critical for decision-making.
“Where is SAR Technology Making the Biggest Impact Today?”
SAR’s versatility is evident in the breadth of its applications. In disaster management, it provides real-time insights during floods, earthquakes, and landslides, often when optical imagery fails. In climate and environmental science, SAR tracks deforestation, ice melt, soil moisture, and land degradation, contributing to global sustainability efforts. The defense sector leverages SAR for persistent surveillance, target recognition, and threat detection in any weather or lighting conditions. In agriculture, SAR supports precision farming by monitoring crop health and yield estimates. It also plays a pivotal role in infrastructure monitoring, detecting early signs of structural deformation in bridges, roads, and dams—preventing costly failures and improving public safety.
What Forces are Powering the Surge in SAR Adoption Worldwide?
A key growth driver is the surging demand for accurate geospatial intelligence by military forces, intelligence agencies, and enterprises across sectors. The rise of cost-effective microsatellites and reusable launch vehicles is making it easier to deploy SAR constellations, vastly improving data coverage and revisit times. Meanwhile, the escalating impacts of climate change are pushing governments and institutions to adopt resilient, weather-independent monitoring solutions like SAR. On the technology side, rapid advancements in AI and data analytics are transforming the complex raw outputs of SAR into clear, actionable insights, dramatically expanding its usability and impact.
How is the SAR Market Structured Across Platforms, Frequencies, and Use Cases?
The SAR market is intricately segmented. Spaceborne SAR dominates, thanks to its ability to provide global coverage and continuous monitoring. Airborne and UAV-based SAR systems are growing in tactical defense and localized environmental scenarios. Frequency segmentation shows that X-band SAR is used for high-resolution imagery, C-band for broad land applications, and L-band for forest and terrain penetration. Application-wise, while defense still commands a significant share, fast-growing segments include agriculture, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure inspection. These new verticals are reshaping SAR’s traditional military-centric landscape into a diversified technology ecosystem.
Which Regions are Leading the Charge in SAR Innovation and Deployment?
North America currently leads the SAR market, thanks to strong military funding and the presence of innovative SAR firms like Capella Space and Maxar. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, India, and Japan, is rapidly emerging as a growth engine, investing heavily in SAR constellations for civil, military, and commercial use. Europe, supported by the European Space Agency and programs like Copernicus, remains a vital hub for SAR innovation and open-access Earth observation data. Meanwhile, regions like Latin America and Africa are beginning to adopt SAR for land management, environmental protection, and disaster resilience initiatives.
How is AI Transforming SAR Data into Actionable Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is unlocking SAR’s full potential. Traditional SAR imagery required expert interpretation and long processing times. Today, AI and machine learning algorithms automate image enhancement, noise reduction, and pattern detection. From identifying illegal constructions and tracking vehicles to monitoring urban sprawl and environmental degradation, AI enables real-time, large-scale analysis. Predictive analytics further allow users to forecast crop yields, assess flood risks, or predict infrastructure failures using SAR data blended with other sources. However, challenges such as data diversity, annotation requirements, and ethical AI deployment still need to be addressed to ensure responsible use.
What’s on the Horizon for Synthetic Aperture Radar Technology?
Looking ahead, SAR is set to become even more accessible, powerful, and integrated. Satellite miniaturization and lower launch costs will continue to drive widespread deployment. SAR-as-a-Service (SaaS) models will democratize access, allowing non-expert users to benefit from processed SAR imagery and analytics. Cloud computing and edge processing will support real-time, on-demand SAR data interpretation. The future will also see the convergence of SAR with other remote sensing technologies like LiDAR, optical, and hyperspectral imaging, offering rich, fused datasets for smarter insights. Applications in smart cities, autonomous navigation, environmental forecasting, and space traffic monitoring are also on the rise, further extending SAR’s utility.
Who are the Key Innovators Defining the SAR Ecosystem?
The SAR market is shaped by a diverse set of global players. Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Thales continue to dominate the defense segment, while companies like AIRBUS and General Atomics offer advanced airborne systems. Commercial pioneers such as ICEYE, Capella Space, and Umbra Lab are redefining data accessibility through small-satellite constellations. Maxar Technologies and L3Harris are integrating SAR data into geospatial intelligence platforms. MetaSensing and IMSAR lead in frequency versatility and lightweight payload design, respectively. This competitive landscape fosters both innovation and affordability, propelling the SAR market forward.
Why Synthetic Aperture Radar is Poised to Revolutionize Earth Observation?
Synthetic Aperture Radar has transcended its military roots to become a linchpin in the future of Earth observation and real-time geospatial intelligence. From national security to food security, urban planning to environmental sustainability, SAR is delivering insights that were once impossible due to technical or environmental limitations. With AI integration, increased data availability, and scalable delivery models, SAR is no longer just a surveillance tool, it’s becoming an everyday resource for governments, enterprises, and researchers alike. The next decade will mark SAR’s evolution from a niche technology into a core infrastructure for global monitoring and decision-making.













