Phototransistors have emerged as a vital component in the world of optoelectronics, finding applications in a wide array of industries due to their ability to detect and respond to light. From consumer electronics to automotive systems and industrial automation, phototransistors are enabling advanced solutions in light sensing and signal processing. As technology evolves, the phototransistor market is poised for significant growth, driven by rising demand for high-performance optical sensors and their increasing integration into modern devices. In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of phototransistors, the factors propelling their market expansion, emerging applications, and the technological advancements shaping their future.
Understanding Phototransistors
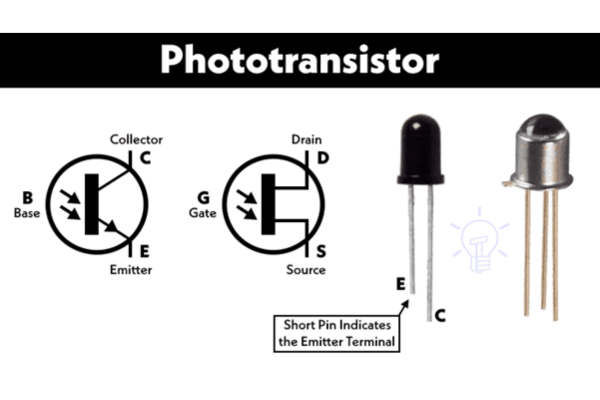
A phototransistor is a type of transistor that operates based on light intensity. Unlike traditional transistors that are controlled by electric current, phototransistors are triggered by photons. When light hits the semiconductor material in the device, it generates a current proportional to the intensity of the light. This ability to convert light signals into electrical signals makes phototransistors ideal for use in light detection and signal amplification applications.
Phototransistors are widely appreciated for their sensitivity, compact size, and cost-effectiveness. They come in various forms, including silicon and compound semiconductor-based designs, catering to specific performance requirements across industries.
Market Drivers
The phototransistor market is growing rapidly, fueled by several key factors:
Rising Demand for Consumer Electronics
The proliferation of smart devices such as smartphones, wearable gadgets, and IoT-enabled products has created a strong demand for phototransistors. These devices rely on optical sensors for functionalities like ambient light sensing, proximity detection, and gesture recognition, driving the adoption of phototransistors in consumer electronics.
Expansion of Automotive Applications
With the advent of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles, the automotive industry has become a major growth driver for phototransistors. Applications such as light sensing for adaptive headlights, rain sensors, and lane detection systems are creating new opportunities for phototransistor manufacturers.
Industrial Automation and IoT Growth
The increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 and IoT technologies is boosting the demand for optical sensors in manufacturing and automation. Phototransistors play a crucial role in systems such as object detection, barcode scanning, and robotic vision, making them indispensable in modern industrial setups.
Emergence of Smart Cities
The push for smart city projects around the globe has driven the need for phototransistors in applications such as smart lighting, traffic management, and environmental monitoring. These sensors are instrumental in improving the efficiency of urban infrastructures.
Advancements in Optoelectronics
Innovations in semiconductor materials and fabrication techniques have led to the development of phototransistors with higher sensitivity, faster response times, and enhanced reliability. This is expanding their usability in high-precision applications like medical devices and scientific instrumentation.
Key Applications of Phototransistors
1. Consumer Electronics
Phototransistors are widely used in devices like smartphones and tablets for automatic screen brightness adjustment, improving user experience and conserving energy.
2. Automotive Sector
From rain sensors for windshield wipers to adaptive lighting systems, phototransistors enhance safety and convenience in vehicles.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, phototransistors are used in pulse oximeters, blood glucose monitors, and other diagnostic devices to enable accurate light-based measurements.
4. Industrial Automation
Phototransistors are integral to optical encoders, position sensors, and machine vision systems, facilitating seamless automation in industrial processes.
5. Security Systems
Optical sensors based on phototransistors are employed in surveillance cameras and motion detectors to improve security infrastructure.
Technological Advancements
The phototransistor market is witnessing significant innovation, with manufacturers focusing on enhancing performance and versatility. Key advancements include:
- Miniaturization: Smaller phototransistors are enabling their integration into compact devices such as wearables and implantable medical devices.
- Wavelength Sensitivity: New designs with sensitivity across a wider range of wavelengths are expanding their applications in areas like UV detection and infrared sensing.
- High-Speed Performance: Improved response times are enabling their use in high-speed communication systems and optical data transmission.
Additionally, the integration of phototransistors with AI and machine learning is paving the way for smarter sensing systems capable of real-time data processing and decision-making.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the phototransistor market is growing, it faces challenges such as intense competition, high R&D costs, and technical limitations like sensitivity to temperature variations. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation.
For instance, developing phototransistors with higher temperature tolerance and energy efficiency can open up new avenues in aerospace and defense applications. Additionally, collaborations between manufacturers and research institutions can accelerate the adoption of phototransistor technologies in untapped markets.
Future Outlook
The global phototransistor market is poised to witness robust growth in the coming years. According to industry reports, the market is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR, driven by advancements in optoelectronics and the expanding adoption of smart technologies. As industries continue to embrace automation and connectivity, the demand for phototransistors will remain strong.
Moreover, the integration of phototransistors into emerging technologies such as LiDAR, augmented reality (AR), and quantum computing promises to unlock exciting possibilities. These advancements will not only drive market expansion but also revolutionize industries that rely on precise light sensing and signal processing.